Modal Window
A modal window is a window that captures the entire focus for the duration of its existance. In other word, when a modal window is started, it will be on top of everything else and the entire input (mouse and keyboard will be treated by it).
When a modal window is opened the rest of the windows or other modal windows will be disabled:
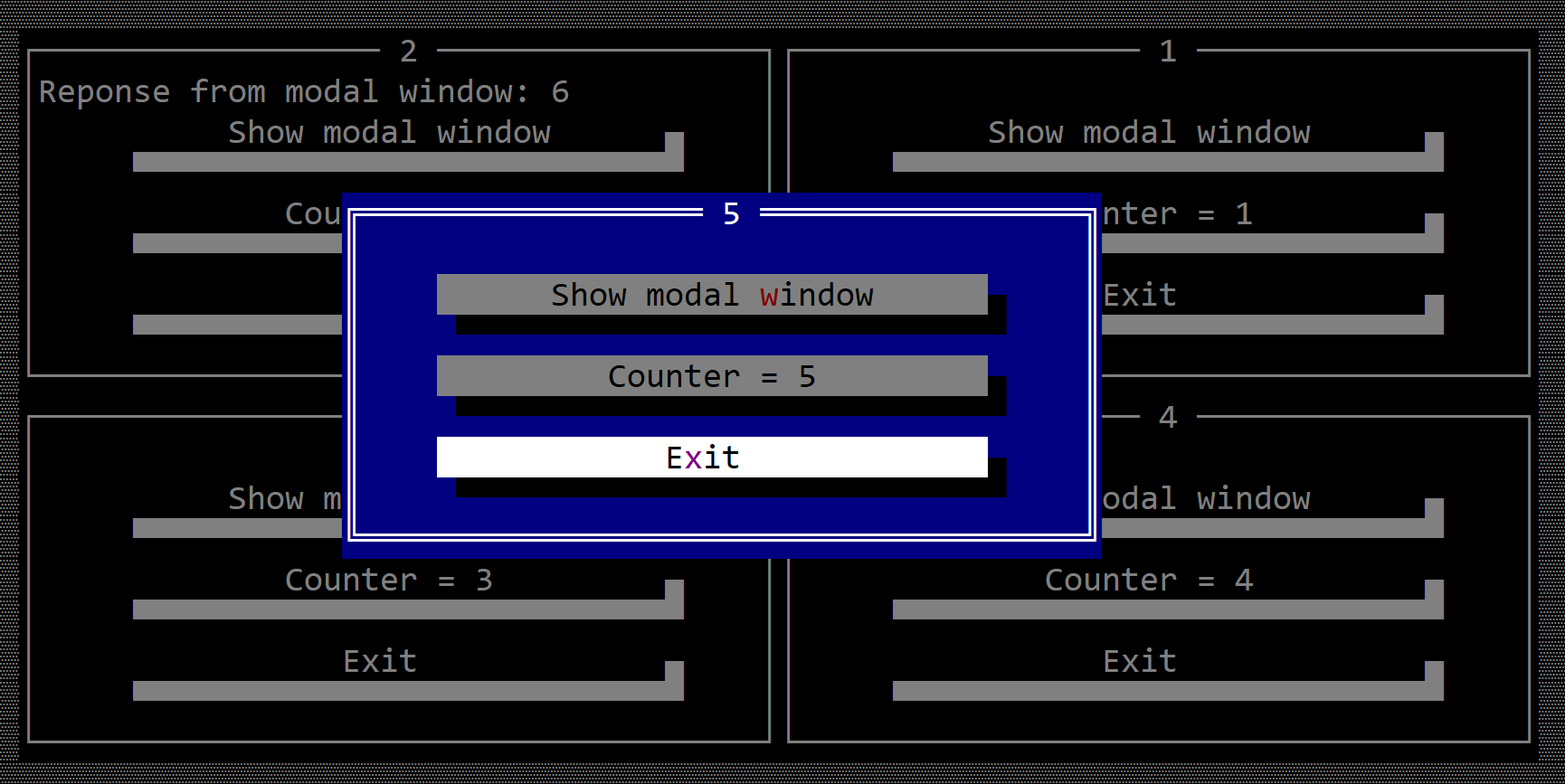
A modal window is in fact just like a regular window (you can add other controls, you can resize and move it) and you can intercept events just like in a regular window case. However, since a modal window can not lose the focus, it has another property (response) that implies that it will provide a response once its execution ends. The response can be any kind of type (including a void type).
To create a modal window that will handle events from its children, use #[ModalWindow(...)] method:
#[ModalWindow(events=..., response=...)]
struct MyModalWindow {
// specific fields
}
Besides the normal methods that a regular Window has, the following extra methods are available:
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
exit() or close() | Exits the current modal window without returning anything. This translates into returning None from the call of method show(...) |
exit_with(...) | Exits and returns a value of the same type as the parameter reponse from the #[ModalWindo(...)] definition. This translates into returning Some(value) from the call of method show(...) |
show() | Shows the modal window and capture the entire input. The execution flow is blocked until method show returns. |
Besides the keys that a regular (non-modal) window supports, the following keys have a different purpose:
| Key | Purpose |
|---|---|
Escape | Trigers a call to on_cancel(...) method. By default this will close the modal window and will return None to the caller. The behavior can be changed by returning ActionRequest::Deny from the on_cancel callback |
Enter | Calls the on_accept(...) method. This will not close the window unless you call exit() or exit_with(...) from within the callback |
To disable this behavior, you can add WindowEvents to the list of events and then return ActionRequest::Deny when implementing on_cancel.
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[ModalWindow(events=WindowEvents, response=...)] struct MyModalWindow { // specific fields } impl WindowEvents for MyWindow { fn on_cancel(&mut self) -> ActionRequest { ActionRequest::Deny } } }
Execution flow
Normaly, a modal window looks like the following template:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { // ResponseType is a type of data that you want to return // it could be anything like: u32, String, something user-defined #[ModalWindow(events=..., response=ResponseType)] struct MyWindow { // specific fields } impl MyWindow { fn new(...) -> MyWindow { /* constructor */ } // other methods } // SomeEvent in this context could be any event supported by a Window // such as: ButtonEvents, ToolBarEvents, ... impl SomeEvent for MyWindow { fn event_methods(&mut self...) { // some operations / checks self.exit_with(ResponseType::new(...)); // ResponseType::new(...) something that creates a new object of type ResponseType } } }
Once all of this is in place, you can start the modal window in the following way:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let r: ResponseType = MyWindow::new(...).show(); }
Example
The following example creates a window with a button that starts a modal window that doubles a value received from the first window.
#[ModalWindow(events=ButtonEvents,response=i32)] struct MyModalWin { value: i32, } impl MyModalWin { fn new(value: i32) -> Self { let mut w = MyModalWin { base: ModalWindow::new("Calc", layout!("a:c,w:40,h:12"), window::Flags::None), value: value * 2, }; w.add(Label::new(format!("{} x 2 = {}", value, value * 2).as_str(), layout!("a:c,w:16,h:1"))); w.add(button!("Close,d:b,w:15")); w } } impl ButtonEvents for MyModalWin { fn on_pressed(&mut self, _handle: Handle<Button>) -> EventProcessStatus { self.exit_with(self.value); EventProcessStatus::Processed } } #[Window(events = ButtonEvents)] struct MyWin { text: Handle<Label>, value: i32, } impl MyWin { fn new() -> Self { let mut win = MyWin { base: window!("'My Win',a:c,w:40,h:16"), text: Handle::None, value: 1, }; win.text = win.add(label!("'Value=10',a:c,w:24,h:1")); win.add(button!("Double,d:b,w:15")); win } } impl ButtonEvents for MyWin { fn on_pressed(&mut self, _handle: Handle<Button>) -> EventProcessStatus { // first run the modal window if let Some(response) = MyModalWin::new(self.value).show() { // set the new value self.value = response; let h = self.text; if let Some(label) = self.control_mut(h) { label.set_caption(format!("Value={}", response).as_str()); } } EventProcessStatus::Processed } } fn main() -> Result<(), appcui::system::Error> { let mut a = App::new().build()?; a.add_window(MyWin::new()); a.run(); Ok(()) }