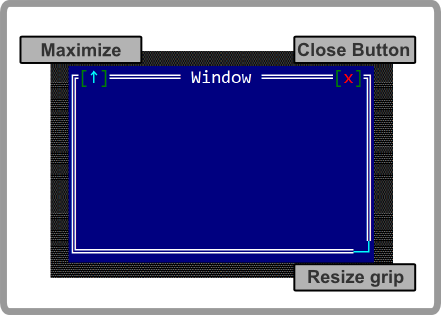
Window
A window is the core component of an application and it is the object where all events from children controls are being processed.
To create a Window use:
Window::newmethod (with 3 parameters: a title, a layout and initialization flags)Window::with_typemethod (with 4 parameters: a title, a layout , initialization flags and a type)- macro
window!.
let w = Window::new("Title", layout!("x:10,y:5,w:15,h:9"),window::Flags::None);
let w2 = window!("Title,a:c,w:10,h:10");
let w3 = window!("title='Some Title',a:c,w:30,h:10,flags=[Sizeable])");
let w4 = window!("title='WithTag',a:c,w:30,h:10,tag:MyTag)");
let w5 = window!("Title,a:c,w:10,h:10,key:Alt+F10");
let w6 = window!("Title,a:c,w:10,h:10,key:auto");
Keep in mind that window will NOT handle any events from its children.
A window supports all common parameters (as they are described in Instantiate via Macros section). Besides them, the following named parameters are also accepted:
| Parameter name | Type | Positional parameter | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
title or text or caption | String | Yes (first postional parameter) | The title (text) of the window |
flags | String or List | No | Window initialization flags |
type | String | No | Window type (visual) |
bg or back or background | String | No | The background of the window. |
tag | String | No | The tag of the window |
hotkey or hot-key or key | Key | No | The hotkey associated with a window. You can also use the auto value to ask the framework to find the first available key (from Alt+1 to Alt+9) |
To create a window that will handle events from its children, use #[Window(...)] method:
#[Window(events=..., )]
struct MyWindow {
// specific fields
}
A window supports the following initialization flags:
window::Flags::None- regular window (with a close button)window::Flags::SizeableorSizeable(for window! macro) - a window that has the resize grip and the maximize buttonwindow::Flags::NoCloseButtonorNoCloseButton(for window! macro) - a window without a close buttonwindow::Flags::FixedPositionorFixedPosition(for window! macro) - a window that can not be moved
the following types:
window::Type::ClassicorClassic(for window! macro) - a regular window with a classic look (double border)window::Type::RoundedorRounded(for window! macro) - a window with rounded cornerswindow::Type::PanelorPanel(for window! macro) - a window with a top bar and no borders
the following backgrounds:
window::Type::NormalorNormal(for window! macro) - a regular window (using the default background color)window::Type::ErrororError(for window! macro) - a window with a red background to indicate an error messagewindow::Type::NotificationorNotification(for window! macro) - a window with a different background designed for notification messageswindow::Type::WarningorWarning(for window! macro) - a window with a different background designed for Warning messages
Methods
Besides the Common methods for all Controls a button also has the following aditional methods:
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
add(...) | Adds a new control as a child control for current window |
control(...) | Returns an immutable reference to a control based on its handle |
control_mut(...) | Returns a mutable reference to a control based on its handle |
request_focus_for_control(...) | Requests the focus for a specific control given a specfic handle |
toolbar() | Returns a mutable reference to current window toolbar |
set_title(...) | Sets the title of Window. Example: win.set_title("Title") - this will set the title of the window to Title |
title() | Returns the title of the current window |
set_tag(...) | Sets the tag of Window. Example: win.set_tag("ABC") - this will set the tag of the window to ABC |
tag() | Returns the tag of the current window |
clear_tag() | Clears the current tag. Its equivalent to set_tag("") |
set_auto_hotkey() | Automatically selects a free hotkey (in a format Alt+{number} where {number} is between 1 and 9) |
enter_resize_mode() | Enters the resize mode programatically |
close | Closes current window |
Key association
In terms of key association, a Window has two modes:
- Normal mode (for whem a window is has focus)
- Resize/Move mode (in this mode you can use arrows and various combinations to move the window)
For normal mode
| Key | Purpose |
|---|---|
Ctrl+Alt+M or Ctrl+Alt+R | Switch the window to resize/move mode |
Escape | Trigers a call cu on_cancel(...) method. By default this will close the window. Howeverm you can change the behavior and return ActionRequest::Deny from the on_cancel callback |
Up or Alt+Up or Ctrl+Up | Moves to the closes control on upper side the curent one. |
Down or Alt+Down or Ctrl+Down | Moves to the closest control on the bottom side of the curent one |
Left or Alt+Left or Ctrl+Left | Moves to the closest control on the left side of the curent one |
Right or Alt+Right or Ctrl+Right | Moves to the closest control on the right side of the curent one |
OBS: Keep in mind that if any of these keys (in particular Left, Right, Up and Down) are capture by one of the children of a window, they will not pe process by the window.
For resize/move mode
| Key | Purpose |
|---|---|
Escape or Enter or Tab or Space | Switch back to the normal mode |
Left, Up, Right, Down | Arrow keys can be used to move the window |
C | Centers the current window to the Desktop |
M or R | Maximizes or Restores the size of the current Windows |
Alt+{Left, Up, Right, Down} | Moves the window towards one of the margins of the Desktop. For example Alt+Up will move current window to the top margin of the client space of the Desktop |
Ctrl+{Left, Up, Right, Down} | Increases or decreases the Width or Height of the current Window |
Events
Window related events can be intercepted via WindowEvents trait. You will need to add WindowEvents in the list of events like in the following example:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[Window(events=WindowEvents)] struct MyWindow { ... } impl WindowEvents for MyWindow { ... } }
WindowEvents is defined in the following way:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { pub trait WindowEvents { fn on_close(&mut self) -> EventProcessStatus { EventProcessStatus::Ignored } fn on_layout_changed(&mut self, old_layout: Rect, new_layout: Rect) {} fn on_activate(&mut self) {} fn on_deactivate(&mut self) {} fn on_accept(&mut self) {} fn on_cancel(&mut self) -> ActionRequest { ActionRequest::Allow } } }
These methods are called under the following scenarious:
| Method | Called when |
|---|---|
on_layout_changed(...) | Called whenever the size or position of a window changes. |
on_activate(...) | Called whenever a window or a modal window receives the focus |
on_deactivate(...) | Called whenever a window or a modal window loses the focus |
on_accept(...) | Called only for modal windows when you hit the Enter key |
on_cancel(...) | For a modal window this method is called when you press Escape. You can use this method to disable closing via Escape key and for an exit with a value (via method exit_with(...)For a regular window (non-modal) this method can be called when you pressed Esc key or when you pressed the close button from a window. |
Window Tags
For every window, a tag can be set for a window (a tag is a string associated with a Window that reflects its purpose). To set a tag use .set_tag("<name") method.
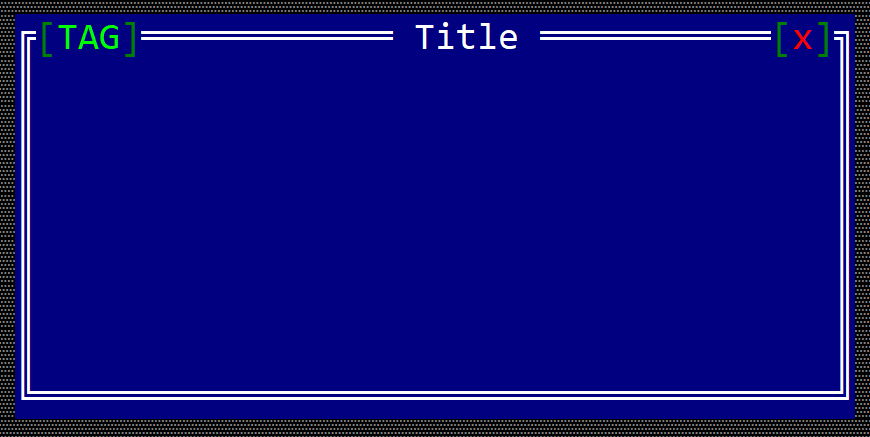
For example, the following code:
fn main() -> Result<(), appcui::system::Error> {
let mut app = App::new().build()?;
let mut win = window!("Title,a:c,w:40,h:9");
win.set_tag("TAG");
app.add_window(win);
app.run();
Ok(())
}
should generate a window that looks like the following:
Window Hot Key
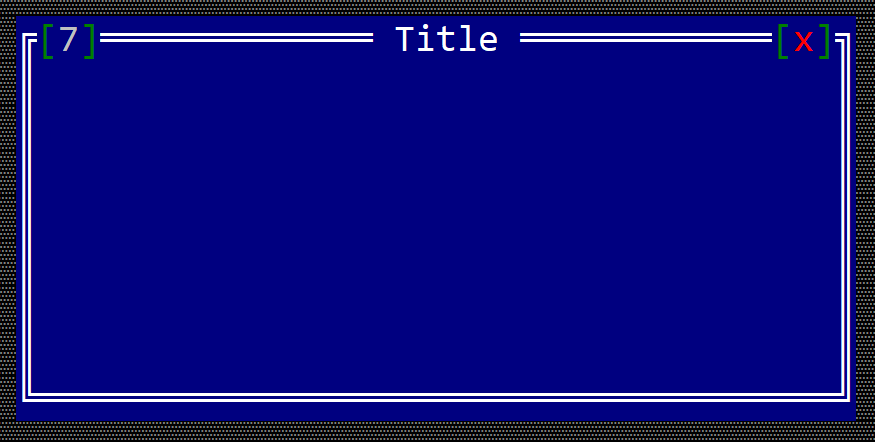
You can also associate a hot key to a window. A hot key allows you to quickly switch between windows. In the next example, we set up Alt+7 as a hot key for a windows.
fn main() -> Result<(), appcui::system::Error> {
let mut app = App::new().build()?;
let mut win = window!("Title,a:c,w:40,h:9");
win.set_hotkey(key!("Alt+7"));
app.add_window(win);
app.run();
Ok(())
}
should generate a window that looks like the following: