GraphView
Represents a graph visualization control that can display nodes and edges with various layout algorithms and interactive features:
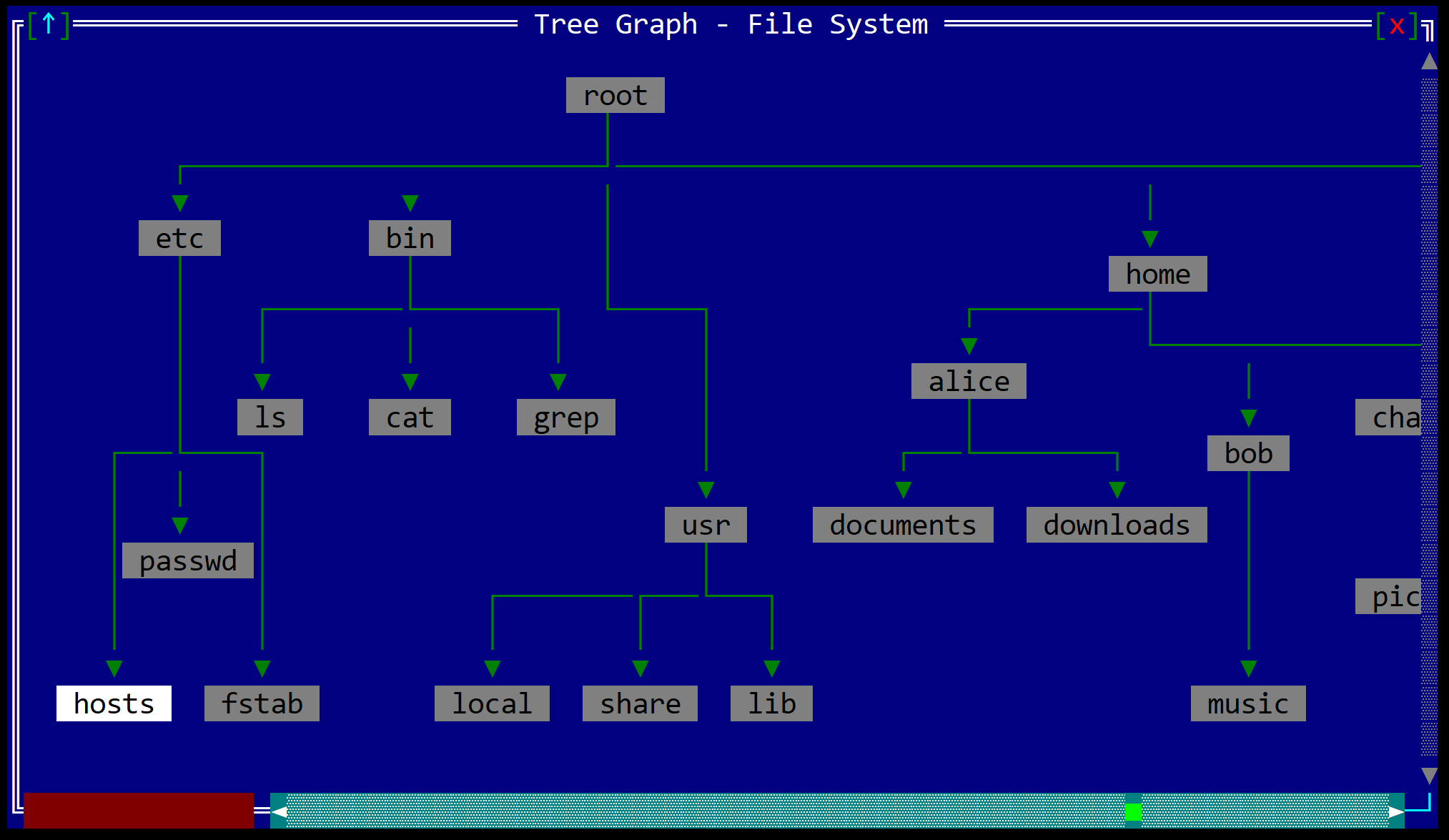
To create a GraphView use GraphView::new method (with 2 parameters: a layout and initialization flags).
let gv = GraphView::new(layout!("x:10,y:5,w:40,h:20"), graphview::Flags::ScrollBars | graphview::Flags::SearchBar);
or the macro graphview!
let gv1 = graphview!("x:10,y:5,w:40,h:20,flags:[ScrollBars,SearchBar]");
let gv2 = graphview!("d:f,arrange:GridPacked,routing:Orthogonal");
A GraphView supports all common parameters (as they are described in Instantiate via Macros section). Besides them, the following named parameters are also accepted:
| Parameter name | Type | Positional parameter | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
flags | List | No | GraphView initialization flags |
background or back | Dict | No | Background character for the GraphView |
left-scroll-margin or lsm | Integer | No | Left margin for scrollbars/search components |
top-scroll-margin or tsm | Integer | No | Top margin for scrollbars/search components |
line-type or edge-line-type or elt | String | No | Line type for drawing edges |
routing or edge-routing | String | No | Edge routing algorithm |
arrange or arrange-nodes | String | No | Node arrangement algorithm |
arrow-heads or arrows | Bool | No | Enable/disable arrow heads on directed edges |
highlight-incoming-edges or hie | Bool | No | Highlight incoming edges of current node |
highlight-outgoing-edges or hoe | Bool | No | Highlight outgoing edges of current node |
A GraphView supports the following initialization flags:
graphview::Flags::ScrollBarsorScrollBars(for macro initialization) - enables scrollbars for navigating large graphs.graphview::Flags::SearchBarorSearchBar(for macro initialization) - enables a search bar for finding nodes.
A GraphView supports the following edge line types:
LineType::SingleorSingle- single line edgesLineType::DoubleorDouble- double line edgesLineType::SingleThickorSingleThick- thick single line edgesLineType::BorderorBorder- border style edgesLineType::AsciiorAscii- ASCII character edgesLineType::AsciiRoundorAsciiRound- ASCII rounded edgesLineType::SingleRoundorSingleRound- single rounded edgesLineType::BrailleorBraille- braille character edges
A GraphView supports the following edge routing algorithms:
graphview::EdgeRouting::DirectorDirect- draw edges as direct lines between nodesgraphview::EdgeRouting::OrthogonalorOrthogonal- draw edges as orthogonal lines (straight lines with right-angled corners) that try to avoid other nodes and edges. This ususally creates a better visual representation of the graph (in particular, for large graphs)
A GraphView supports the following node arrangement algorithms:
graphview::ArrangeMethod::NoneorNone- no automatic arrangement (use custom positions)graphview::ArrangeMethod::GridorGrid- arrange nodes in a grid with spacinggraphview::ArrangeMethod::GridPackedorGridPacked- arrange nodes in a compact gridgraphview::ArrangeMethod::CircularorCircular- arrange nodes in a circlegraphview::ArrangeMethod::HierarchicalorHierarchical- arrange nodes hierarchically with spacinggraphview::ArrangeMethod::HierarchicalPackedorHierarchicalPacked- arrange nodes hierarchically, compactlygraphview::ArrangeMethod::ForceDirectedorForceDirected- use force-directed layout algorithm
Some examples that use these parameters:
let search_enabled = graphview!("x:0,y:0,w:50,h:30,flags:[SearchBar]");
let styled_graph = graphview!("d:f,line-type:Double,routing:Orthogonal,arrange:Circular,arrows:true");
let highlighted = graphview!("d:f,hie:true,hoe:true,back:{.,gray,black}");
Events
To intercept events from a GraphView, the following trait has to be implemented on the Window that processes the event loop:
pub trait GraphViewEvents<T> {
fn on_current_node_changed(&mut self, handle: Handle<GraphView<T>>) -> EventProcessStatus {...}
fn on_node_action(&mut self, handle: Handle<GraphView<T>>, node_index: usize) -> EventProcessStatus {...}
}
Methods
Besides the Common methods for all Controls a GraphView also has the following additional methods:
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
set_graph(...) | Sets the graph data to be displayed. Takes a Graph<T> object containing nodes and edges. |
graph() | Returns a reference to the current graph data. |
set_background(...) | Sets the background character for the GraphView. |
clear_background() | Clears the background character, making it transparent. |
set_edge_routing(...) | Sets the edge routing algorithm (Direct or Orthogonal). |
set_edge_line_type(...) | Sets the line type used for drawing edges. |
enable_edge_highlighting(...) | Enables or disables highlighting of incoming and outgoing edges for the current node. Takes two boolean parameters: incoming and outgoing. |
enable_arrow_heads(...) | Enables or disables arrow heads on directed edges. |
arrange_nodes(...) | Applies a layout algorithm to arrange the nodes in the graph. Takes an ArrangeMethod parameter. |
Graph Methods
The graph object returned by graph() provides additional methods for accessing graph data:
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
current_node_id() | Returns the index of the currently selected node, or None if the graph is empty. |
current_node() | Returns a reference to the currently selected node, or None if the graph is empty. |
node(index) | Returns a reference to the node at the specified index, or None if the index is invalid. |
nodes_count() | Returns the total number of nodes in the graph. |
Node Methods
Node objects provide access to their contained data:
| Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
value() | Returns a reference to the data object (of type T) contained in the node. |
Key association
The following keys are processed by a GraphView control if it has focus:
| Key | Purpose |
|---|---|
Arrow Keys | Navigate between nodes in the specified direction (finds the closest node in that direction). |
Ctrl+Arrow Keys | Move the current node by one position in the specified direction. |
Enter | Triggers a node action event (on_node_action) for the current node. |
Ctrl+Tab | Move to the next node in the graph (by index). |
Ctrl+Shift+Tab | Move to the previous node in the graph (by index). |
Alt+Arrow Keys | Scroll the view in the specified direction (when scrollbars are enabled). |
Page Up/Page Down | Scroll the view up or down by one page. |
Home | Scroll to the top-left of the graph. |
End | Scroll to the bottom-right of the graph. |
Escape | Clear search text (if search bar is active), or exit search mode. |
Enter (in search) | Go to next matching node. |
Ctrl+Enter (in search) | Go to previous matching node. |
Mouse interaction
The GraphView supports various mouse interactions:
- Click: Select a node by clicking on it
- Double-click: Trigger a node action event for the clicked node
- Drag: Move nodes by dragging them, or scroll the view by dragging empty space
- Mouse wheel: Scroll the view in the specified direction
- Hover: Highlight nodes when hovering over them
Graph item
A GraphView can display a graph data structure. The graph data structure is a collection of nodes and edges. Each node can contain a data object of type T that must implement the GraphNode trait.
pub trait GraphNode {
fn write_label(&self, f: &mut dyn std::fmt::Write, size: Size) -> std::fmt::Result;
fn write_description(&self, f: &mut dyn std::fmt::Write) -> std::fmt::Result {
Ok(())
}
fn prefered_size(&self) -> Size;
}
where:
write_labelis used to write the label of the node to the formatter (this method is required and must be implemented by the data object)write_descriptionis used to write the description of the node. This is an optional method that if implmented is being used to display a tooltip when the user hovers over the node.prefered_sizeis used to get the preferred size of the node. This method is being used when a graph is provided without an explicit size for a node.
Remarks: By default, the GraphNode trait is implemented for the following types:
&strStringu8,u16,u32,u64,usizei8,i16,i32,i64,isize
Creating a graph
A graph can be created in several ways:
- Using the
Graph::newmethod (and providing a vector of nodes and a vector of edges)let graph = Graph::new(nodes, edges); - Using the
Graph::with_slicesmethod (and providing slices of nodes and edges)let graph = Graph::with_slices(nodes, edges, directed); - Using the
Graph::with_slices_and_bordermethod (and providing slices of nodes and edges, and a border type)let graph = Graph::with_slices_and_border(nodes, edges, border, directed);
To create a node (that will further be used in the graph) you can use the NodeBuilder struct.
let node = NodeBuilder::new(node_data).build();
with the following buiolder methods:
size- the size of the node (if not provided, the preferred size as it is returned by theGraphNodeimplementation will be used)position- the position of the node (if not provided, the node will be placed at the top-left corner of the graph)border- the border type for the node (if not provided, no border will be drawn)text_alignment- the text alignment for the node (if not provided, the text will be centered)text_attribute- the text attribute for the node (if not provided, the text will be displayed in the default attribute extracted from the terminal theme)
Similarly, to create an edge (that will further be used in the graph) you can use the EdgeBuilder struct.
let edge = EdgeBuilder::new(from, to).build();
with the following builder methods:
directed- if the edge is directed (with an arrow) or not (if not provided, the edge will be undirected)attribute- the attribute for the edge (if not provided, the edge will be displayed in the default attribute extracted from the terminal theme)line_type- the line type for the edge (if not provided, the default line type will be used)
When building an edge, the from and to parameters are the indices of the nodes in the graph. For example, ina graph with 5 nodes, the edge from node 2 to node 4 will be created with EdgeBuilder::new(2, 4).build() (note that the indices are 0-based).
Some examples on how to create a graph:
- A simple graph with 5 nodes and 4 edges (using slices):
let graph = Graph::with_slices( &["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"], // nodes (of type &str) &[(0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 3), (2, 4)], // edges between nodes true // directed edges ); - A graph with a border around each node:
let graph = Graph::with_slices_and_border( &["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"], // nodes (of type &str) &[(0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 3), (2, 4)], // edges between nodes LineType::Double, // border type true // directed edges ); - A mode complex graph where each node is created manually:
let nodes = vec![ NodeBuilder::new("A").size(Size::new(10, 1)).build(), NodeBuilder::new("B").build(), NodeBuilder::new("C").text_alignment(TextAlignment::Left).build(), NodeBuilder::new("D").text_alignment(TextAlignment::Right).build(), NodeBuilder::new("E").border(LineType::Ascii).build(), ]; let edges = vec![ EdgeBuilder::new(0, 1).build(), EdgeBuilder::new(0, 2).build(), EdgeBuilder::new(1, 3).build(), EdgeBuilder::new(2, 4).build(), ]; let graph = Graph::new(nodes, edges);
Example
The following code creates a window with a GraphView displaying a simple hierarchy. When nodes are selected or activated, the window title updates to show the current action.
use appcui::prelude::*;
type NodeValue = &'static str;
#[Window(events = GraphViewEvents<NodeValue>)]
struct MyWin {
graph_view: Handle<GraphView<NodeValue>>,
}
impl MyWin {
fn new() -> Self {
let mut win = MyWin {
base: Window::new("Graph Demo", layout!("d:f"), window::Flags::None),
graph_view: Handle::None,
};
// Create a simple graph
let nodes = &["Root", "Child 1", "Child 2", "Grandchild"];
let edges = &[(0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 3)];
let graph = graphview::Graph::with_slices(nodes, edges, true);
// Create and configure the GraphView
let mut gv = graphview!("d:f,arrange:Grid,routing:Orthogonal,arrows:true,flags:[ScrollBars,SearchBar],hie:true");
gv.set_graph(graph);
win.graph_view = win.add(gv);
win
}
}
impl GraphViewEvents<NodeValue> for MyWin {
fn on_current_node_changed(&mut self, handle: Handle<GraphView<&'static str>>) -> EventProcessStatus {
if let Some(gv) = self.control(handle) {
if let Some(node) = gv.graph().current_node() {
let title = format!("Graph Demo - Selected: {}", node.value());
self.set_title(&title);
}
}
EventProcessStatus::Processed
}
fn on_node_action(&mut self, handle: Handle<GraphView<&'static str>>, node_index: usize) -> EventProcessStatus {
if let Some(gv) = self.control(handle) {
if let Some(node) = gv.graph().node(node_index) {
let title = format!("Graph Demo - Action on: {}", node.value());
self.set_title(&title);
}
}
EventProcessStatus::Processed
}
}
fn main() -> Result<(), appcui::system::Error> {
let mut app = App::new().build()?;
app.add_window(MyWin::new());
app.run();
Ok(())
}